24 - 30 SEPTEMBER 1997 - THE CUT-OFF STAGE
by KNMI
Synoptic situation
|
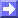
26 September 1997/23.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; green: equivalent thickness 500/850 hPa, red: height contours 500 hPa
|
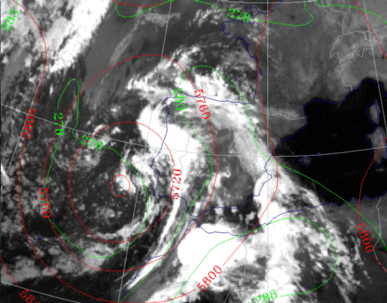
27 September 1997/00.00 UTC - Surface chart; accumulated precipitation 12.00 - 00.00 UTC
|
|
|
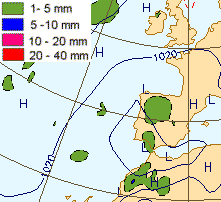
27 September 1997/00.00 UTC
Analysis of the system|
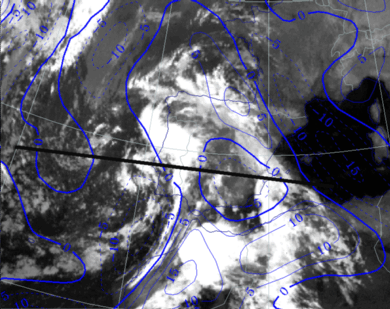
26 September 1997/23.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; blue: thermal front parameter (TFP) 500/850 hPa; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
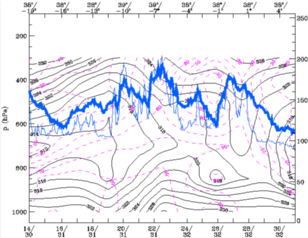
27 September 1997/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative humidity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
The unstable layer over the main land of the peninsula is still present.
|
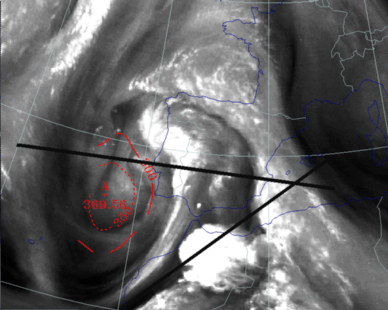
26 September 1997/23.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; red: height of PV=2 units; position of vertical cross sections indicated
|
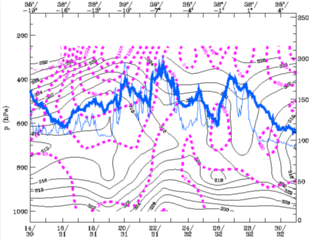
27 September 1997/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative vorticity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
Vorticity in the centre has become stronger as it can be seen in the cross section along the 38° latitude.
24 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black thin: divergence, black thick: convergence, magenta thick: vertical motion (omega) -
upward motion, magenta thin: vertical motion (omega) - downward motion, blue thin: IR pixel values, blue thick: WV pixel values
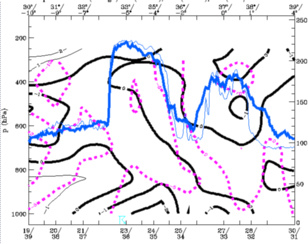
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC
Analysis of the system|
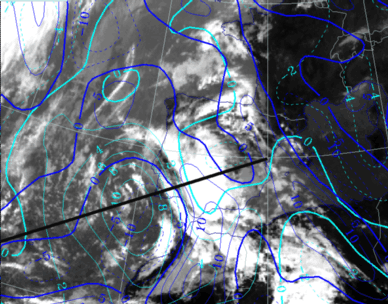
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; blue: thermal front parameter (TFP) 500/850 hPa, cyan: vorticity 500 hPa; position of vertical
cross section indicated
|
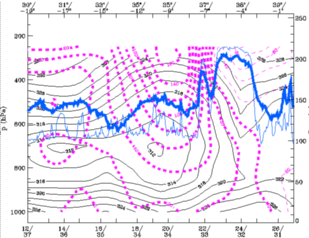
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative vorticity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
|
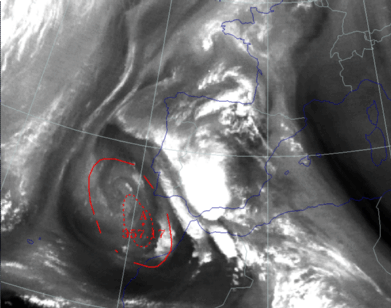
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; red: height of PV=2 units
|
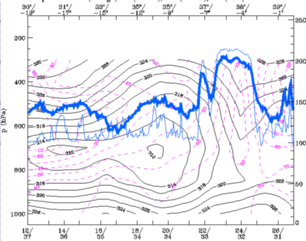
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative humidity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
The instability of the airmas can still be observed in the lower levels in the ThetaE pattern.
|
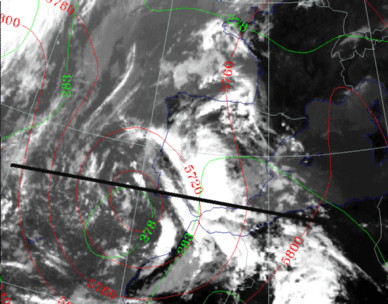
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; green: equivalent thickness 500/850 hPa, red: height contours 500 hPa; position of vertical cross
section indicated
|
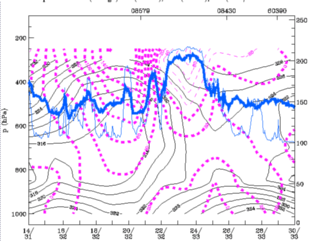
27 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative vorticity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
28 September 1997/00.00 UTC
Analysis of the system|
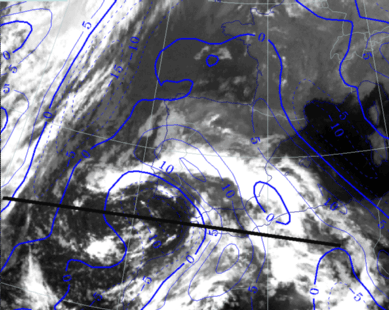
27 September 1997/23.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; blue: thermal front parameter (TFP) 500/850 hPa; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
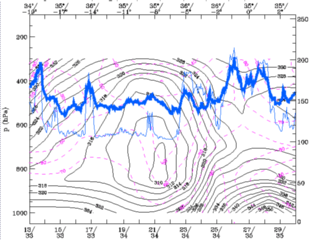
28 September 1997/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative humidity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
Ahead of this gradient zone the air is highly unstable up to 600 hPa.
|
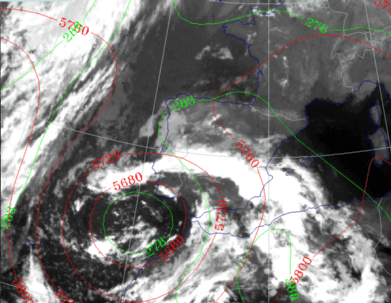
27 September 1997/23.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; green: equivalent thickness 500/850 hPa, red: height contours 500 hPa
|
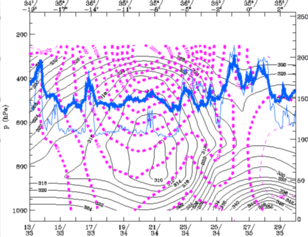
28 September 1997/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative vorticity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
|
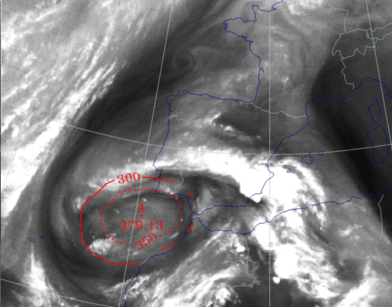
27 September 1997/23.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; red: height of PV=2 units
|
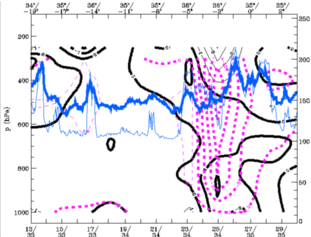
28 September 1997/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section black thin: divergence, black thick: convergence, magenta thick: vertical motion (omega) -
upward motion, magenta thin: vertical motion (omega) - downward motion, blue thin: IR pixel values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
28 September 1997/12.00 UTC
|
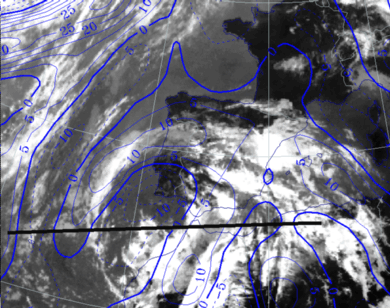
28 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; blue: thermal front parameter (TFP) 500/850 hPa; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
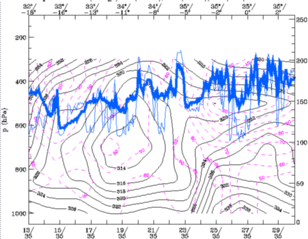
28 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative humidity, blue thin: IR pixel
values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
In the cross section a very dry layer is seen around 600 hPa in the eastern part of the cross section in an area with high cloud tops. The dry layer lies above a very deep developed unstable layer which indicates strong potential instability. In the visible image (not shown) the reflection of short wave (solar) radiation is less in that area indicating only a thin cirrus layer.
|
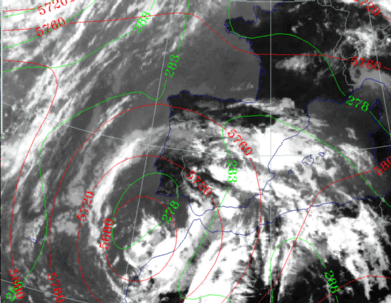
26 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; green: equivalent thickness 500/850 hPa, red: height contours 500 hPa
|
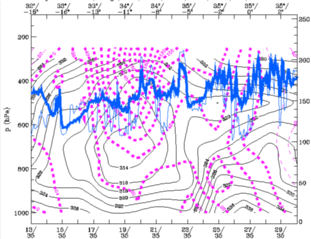
26 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta: relative vorticity, blue thin: IR pixel values,
blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
Vorticity in the centre is still strong, but less than 12 hours earlier, as can be seen in the cross sections.
|
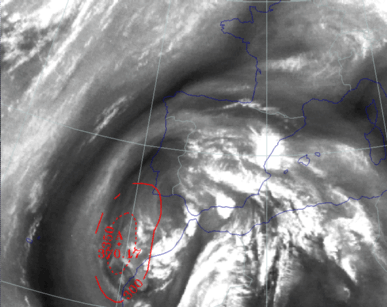
28 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; red: height of PV=2 units
|
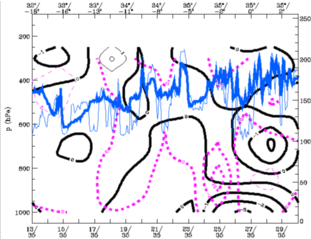
28 September 1997/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section black thin: divergence, black thick: convergence, magenta thick: vertical motion (omega) -
upward motion, magenta thin: vertical motion (omega) - downward motion, blue thin: IR pixel values, blue thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|