Convective Cloud Features In Typical Synoptic Environments: Fair Weather Conditions - Key Parameters
by ZAMG
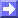
- Height contours 1000 hPa and 500 hPa:
- In contrast to front related convection, development can take place within a low and upper level ridge
- Weak pressure gradient
- No large scale upward motion or forcing within the ridge
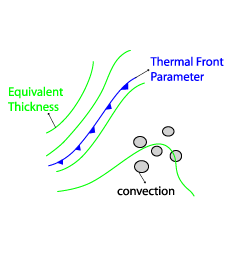
- Thermal front parameter (TFP) and equivalent thickness:
- initiation of convection in clear weather is not related to a significant gradient of equivalent thickness nor any distinct Thermal Front Parameter
- Equivalent potential Temperature at 850 hPa:
- ridge and/or a maximum of ThetaE 850 hPa
- Showalter Index:
- unstable stratification over the area of interest indicated by the Showalter Index 500/850 hPa
- the diurnal variation of the instability indicated by the Showalter index is a result of the diurnal cycle of the available insolation.
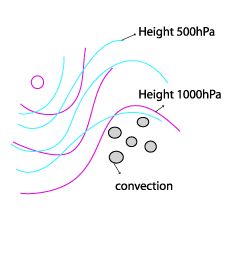
Height contours 1000 hPa and 500 hPa
|
28 July 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR 10.8 image; magenta: height contours 1000 hPa, cyan: height contours 500 hPa
|
|
|
|
Thermal Front Parameter (TFP) and Equivalent Thickness
|
28 July 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR10.8 image; blue: thermal front parameter (TFP) 500/850 hPa, green:
equivalent thickness 500/850 hPa
|
|
|
|
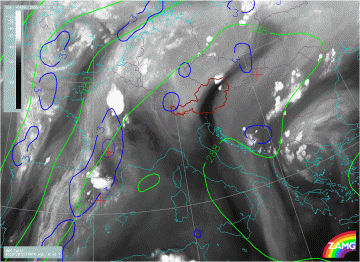
Equivalent Potential Temperature at 850 hPa
|
28 July 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR10.8 image; magenta: equivalent potential temperature 850 hPa
|
|
|

|
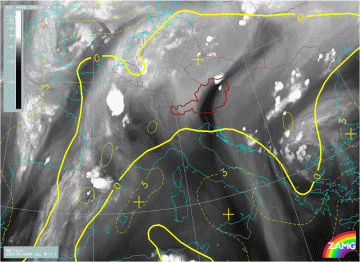
Showalter Index
|
28 July 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR10.8 image; yellow: Showalter index 500/850 hPa
|
|
|
|
Parameters computed and shown in Meso-Scale
ALADIN model forecast fields:ALADIN model fields are computed with a higher spatial resolution (average distance between grid points is about 10km than ECMWF model fields (about 40km. Therefore, meso-scale dynamics of convection can be shown in more detail.
Fields of divergence and vertical motion show a diurnal life cycle:
Divergence
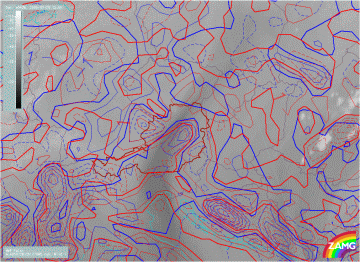
No significant convergence or weak divergence at low levels and weak convergence at higher levels at morning hours. With beginning of convection, there is distinct convergence at lower levels and divergence at higher levels.
|
28 July 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 WV 6.2 image; red dashed: convergence 850 hPa, blue dashed: convergence 700 hPa
|
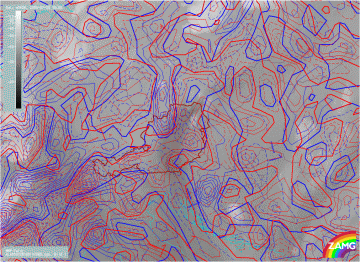
28 July 2005/18.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 WV 6.2 image; red dashed: convergence 850 hPa, blue dashed: convergence 700 hPa
|
|
|
Six hours later (image above), as the cells have already reached mature stage and are dying out due to the subsidence, the opposite is observed. At 850 hPa now divergence is observed (red) and at 700 hPa convergence (blue dashed lines) is observed.
Vertical motion
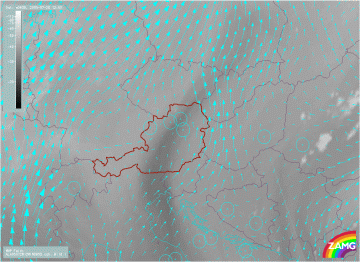
A strong upward motion at lower levels (for instance 850 hPa) indicates convection.
|
28 July 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 WV 6.2 image; cyan:wind vectors at 850 hPa
|
|
|
Although the above model fields show a good correspondence with the convective activity observed in the satellite images that is about to start here, there is unfortunately no indication of the time when convection might start. The initiation of convection still seems best indicated by the WV features described above (see Cloud structure in satellite images).