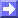
Convective Cloud Features In Typical Synoptic Environments: The Warm Sector - Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
by ZAMG
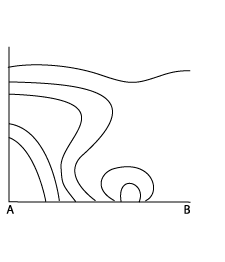
- The isentropes of equivalent potential temperature show a super adiabatic behaviour at mid-levels of the troposphere. A colder air mass overruns the lower warm air mass, resulting in unstable stratification.
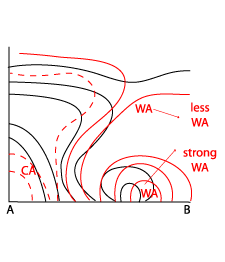
- The vertical distribution of temperature advection is clearly characterised by warm advection at low and mid-levels of the troposphere and cold advection above.
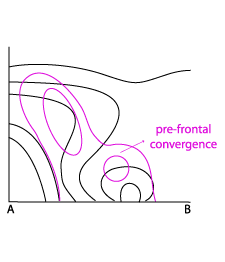
- In the field of divergence, there is typically a convergence maximum at lower levels ahead of the frontal gradient of isentropes.
08 August 2004/18.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
Isentropes
|
08 August 2004/18.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; lines: black: isentropes (ThetaE)
|
|
|
|
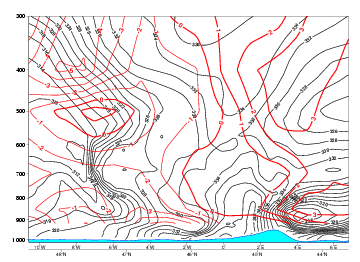
Temperature Advection
|
08 August 2004/18.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; lines: black: isentropes (ThetaE), red: temperature advection
|
|
|
|
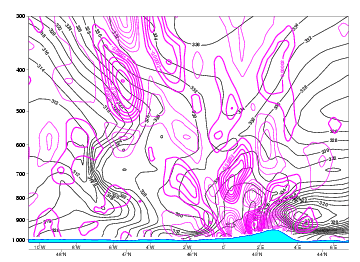
Divergence
|
08 August 2004/18.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; lines: black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta thin: divergence/convergence
|
|
|
|
WA is associated to the MCSs and will contribute slightly to the upward motions. Not surprising, WA is found ahead and aloft of the Cold Front in the area of the Warm sector.
In the divergence field a pronounced maxima of convergence can be seen near the surface in the area of the warm sector. Aloft there is divergence causing outflow of air.